Indexes
Like we learnt in the disks section, the storage is split into blocks and all IO happens at the block level.
This means, when a row is written to disk, we must read the entire block and then update its content and write back the entire block to disk and if we need to read this row again, we need to load all blocks into memory and then find out which block contains the row.
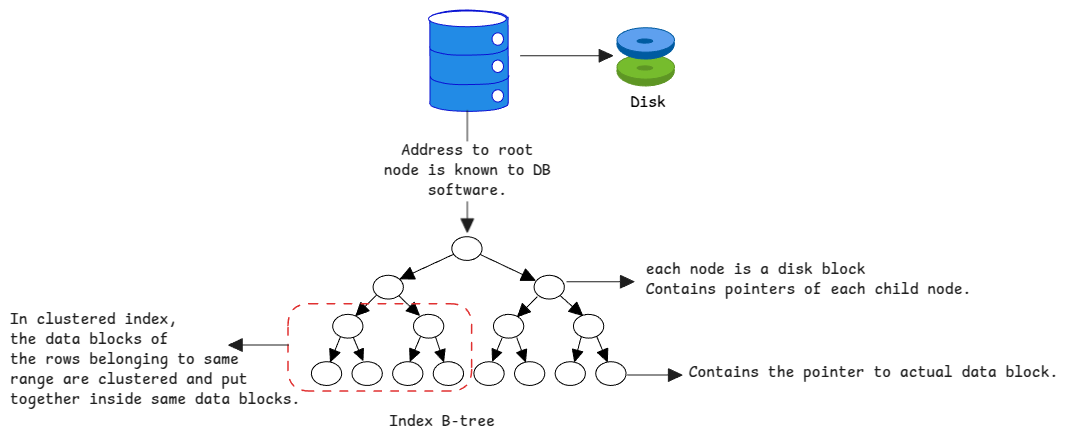
With index, we only load the index data into memory and then we can find out the block which contains the row. The index is a data structure which contains the mapping between the row and the memory address of block on the disk.
Data Structures for Indexes
With the invent of b-trees, the indexes are now stored in a tree structure. This means, we can traverse the tree to find out the actual disk block which contains the row.
Normally when we speak about b-trees, we refer to the in-memory data structure. Where the address are the memory addresses. But in case of database, the addresses are the disk block addresses.
b-tree provides a log(n) time complexity for searching, inserting and deleting. This is much better than the linear search which has a time complexity of O(n).
This is necessary because every add, delete and update must update the index tree as well.
Sorting of index
B-trees maintain sorted data, allowing for efficient range queries. The keys in the B-tree are stored in a sorted order,
The indexes have the keys sorted and stored. But the actual data can be stored anywhere on the disk.
Only in case of clustered indexes, the data is stored in the order of index.
Size of B-tree Nodes
Each node of the B-tree is again size of the disk's block size which is also known as page size.
This means, the number of child node addresses each index node can store depends on the size of the block.
Even though b-tree is a data structure, the full b-tree isn't serialized onto disk or de-serialized into memory.
Instead, only the root node of each index is stored in a specific location where all metadata is stored.
After that each child node is loaded from disk based on the query.
Clustered Indexes
It's the type of index where the data is 'clustered' together in the order of index.
If an index node in the tree points to a specific range of key, all the data in that range is stored in the stored together.
Whether a primary index is by default clustered or no is a database feature. Some databases such as MySQL have clustered primary indexes by default.
The physical order of rows on disk matches the index order. Only one clustered index per table is possible.
Non clustered Indexes
In this type of index, the data isn't stored in order. They can be put in any data block.
All secondary indexes are non clustered indexes.