JSON-LD
JSON Linked Data is a JSON based payload where
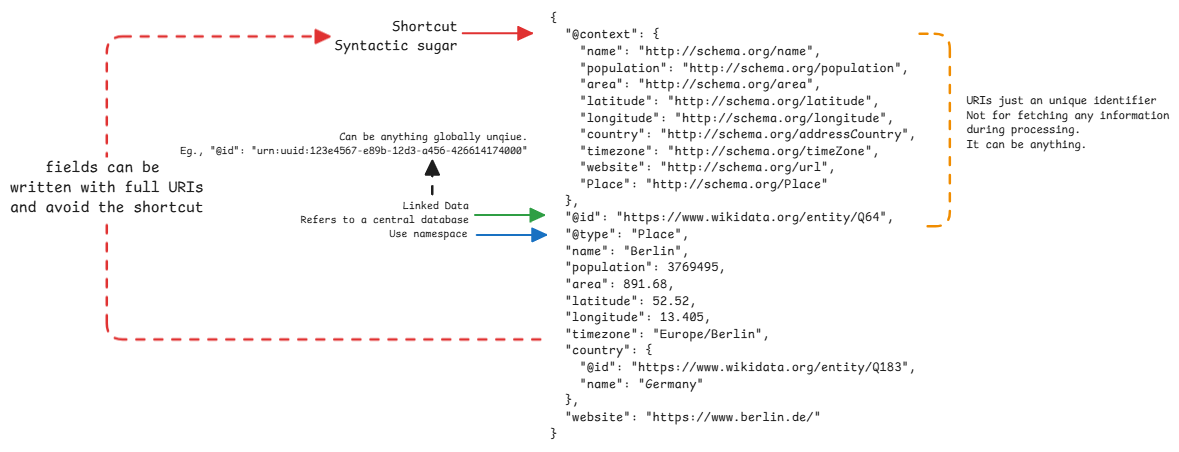
- Data can be referred/linked from other sources. This will ensure that same data is referred from multiple places. This is the @Id field in JSON-LD.
- Meanings of data can be central. The field name can be anything, but we just say what it means by using @context. This is where the word machine-understandable comes from.
It's mainly for global interoperability of data across different systems. For example, multiple organization can share common data definitions in a central place and refer to them in their own data models with any names they wish.
It's coming from a concept called Semantic Web where data is linked across different sources on the web.
JSON-LD versus RDF
RDF (Resource Description Framework) is an abstract data model for representing linked data. Which means, it allows us to represent data as a graph of relationships. RDF represents data as triples: subject, predicate (property/relationship), object. Everything is a 3-tuple.
- Every entity (subject or object) can be identified globally via a URI. (IDs)
- Predicates (properties) are also URIs, giving them precise, machine-readable meaning (Context).
JSON-LD is one of the implementations and serialization methods of RDF. So JSON-LD is a way to represent RDF data model in JSON format.
It's very important to understand that the IDs here are URIs and not URLs. They look like URLs can also be resolved but they're just unique identifiers.
- subject is the @Id in JSON-LD..
- predicate is the field name.
- object is the field value.
NOTE: @type is a special predicate in RDF which is also used in JSON-LD.
Differences to JSON Schema
- JSON schema is about specific data model with constraints and validations while JSON-LD is about linking data across different sources.
- JSON uses fixed field names.
- JSON can't refer to external data
- HATE-OS in REST APIs only provide URIs to access data, but not the data itself.
In Hate-OS, the clients must use the links to fetch or do other actions on the resource. But in JSON-LD, they URIs just refer to other resources from other sources. The clients can still use the data in the payload directly.
Important Fields in JSON-LD
- @context: defines the meaning of different properties of the object. Usually every field has a context defined. The context can be defined locally or refer to an external source.
- @id: defines the unique identifier of the resource. This refers to any resource, anywhere on the web or local. It's the subject.
- @type: defines the meaning/type of the object itself.
- "vocab: When used, call fields are simply referred directly from this vocab. Again the client doesn't go the URL mentioned here, instead implicitly takes the context URI of the field name as 'vocab URI + field name'.