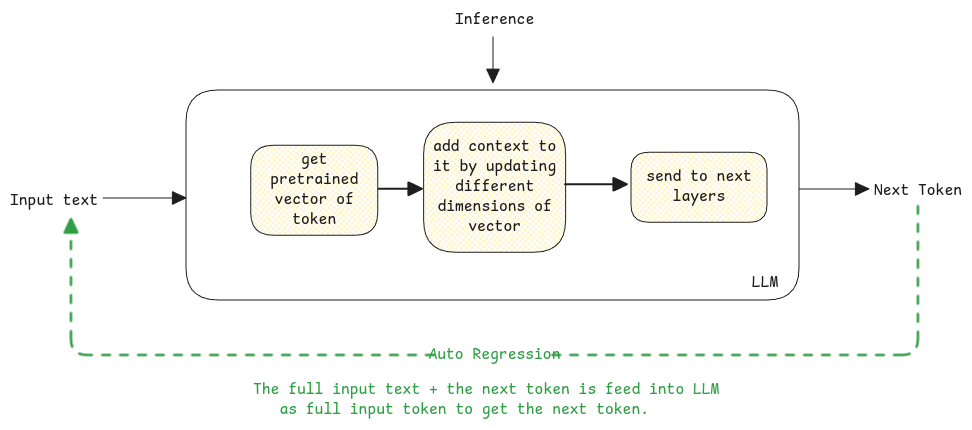
Next Token Prediction
Output in an LLM is always about predicting the next best token a.k.a the next word.
Example - Which is the capital of France?
The output will be next best word after the full text that is, Which is the capital of France? {$answer token}.
Like, this the entire input + generated token (word by word) is passed to LLM to generate the next best word until the full output is generated.
Probability
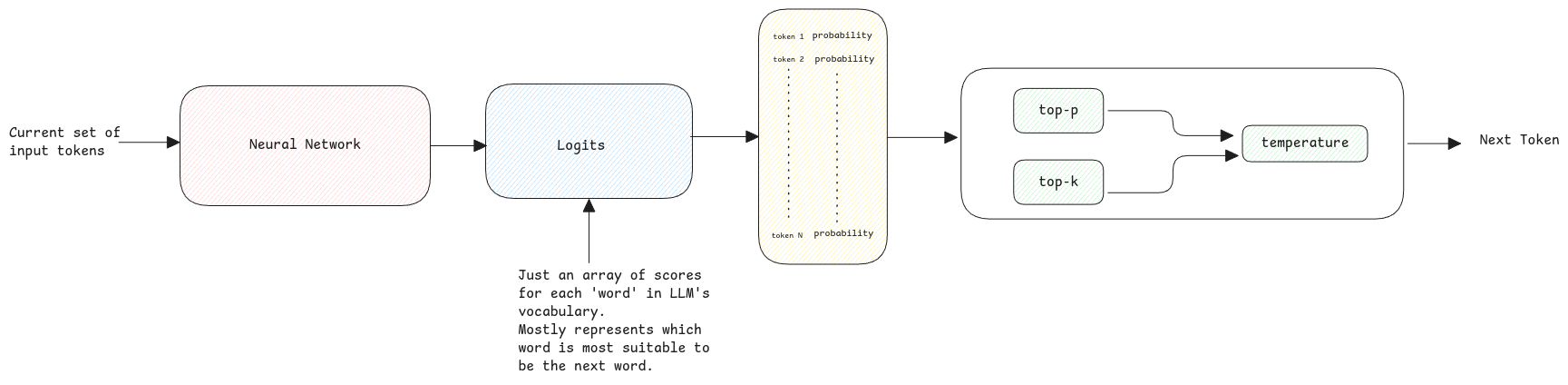
The output of the neural network computation will always be another array of floating values for each token in the LLM's vocabulary.
This value is then converted into probabilities.
Sampling
Sampling is a method in statistics where a subset of items are used to predict the whole.
In case of LLM, the sampling is done from the probability distribution of the next token. Takes only a subset of tokens based on temperature, Top-P, and Top-K values.
-
Temperature: Depending on the this parameter, the LLM decide to chose the token from the list generated. The higher the temperature, the more random the output. The lowest temperature (0.0), the value with the highest probability is always returned.
-
Top-P: This is another parameter that decides the number of tokens to be considered for the output. Using this value, LLM then only considers the top-P tokens sum of whose probabilities is equal to the top-P value.
-
Top-K: Just considered the top-K tokens with the highest probability for the next token.
Greedy Decoding
When greedy decoding is used, the model always selects the token with the highest probability as the next token. For example, temperature with value 0.0, Top-P with value 0.0, and Top-K with value 1.0.
LLMs only knows the relationship between two things. They don't know the cause-effect relationship