Hash Tables
Hash table is a data structure which has an array as it's underlying data structure. This the core data structure and other languages implement it with other names. Java for example has HashMap and HashSet as two different implementations of it and Python has dict which is nothing but Java's HashMap.
Because unlike a linked list or a tree, here since array is used, it has a flat table like structure to store data.
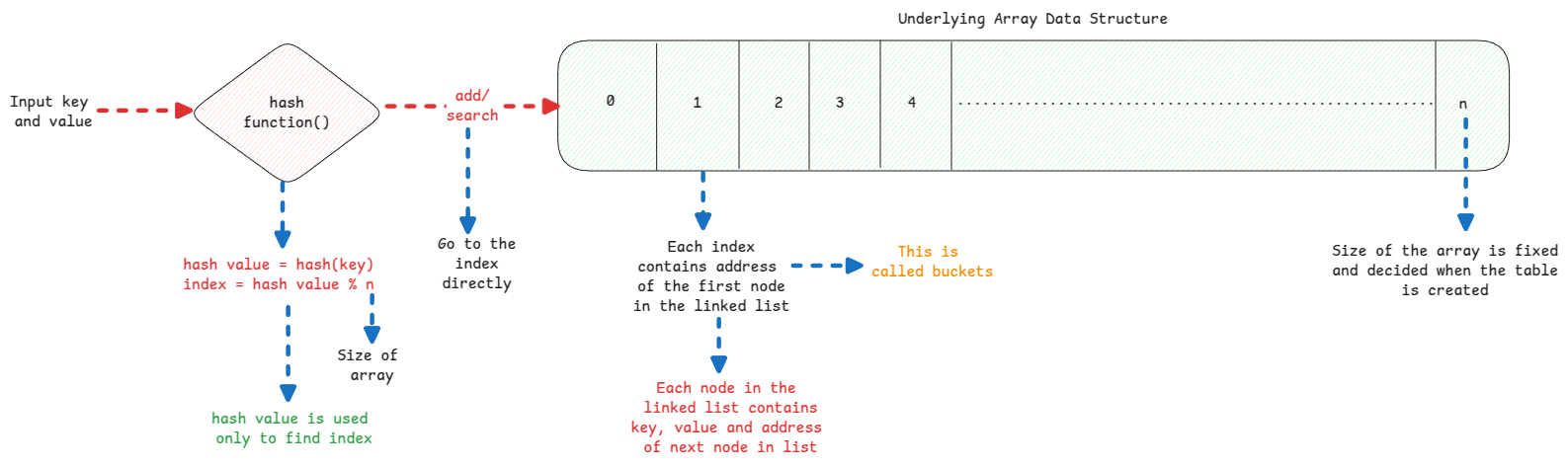
We need linked list in each index to handle collisions. Multiple keys leading to same hash and eventually to same index must be added to the same slot.
Implementation in Java
- The key class's hash() method is used to get the index of the array where the key-value pair must be stored.
- The HashMap has Node[] as it's underlying array.
- This Node is nothing but an implementation of Entry() interface.
- This Entry has - key, value, link to next Node/Entry object.
- During search(key), hash() method is used to get the index of the array where this key can be searched. Then loops through the Entry object stored in that index and uses the equal() method of the key's class to get the correct entry.
If the size of the hash table isn't selected correctly, then more keys get hashed to same index and this leads to increase of linked list size. This degrades the performance because the search must through entire list and put() must loop through entire list to figure the last entry in the linked list to add the new entry.
HashSet()
This is exactly same as HashMap() but the only difference is that it doesn't hold any values. The HashSet() simply uses a dummy value PRESENT as the value in all the Entry() object.