Object References
References in Java is an abstract handle. This means, it points to a memory address in heap but the JVM ensures that the internal details aren't exposed. There is no way we can get the actual address.
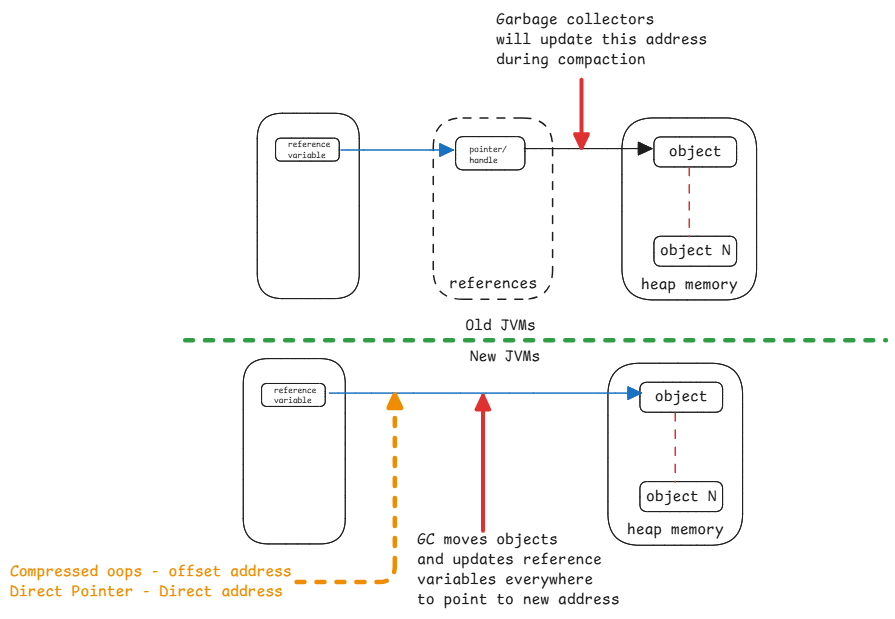
Java has provided different ways to link the reference variable to the actual address in memory. This means, the reference variable has offset address, direct address, etc.
But all of these have the same abstract implementation. We can't get the internal reference details.
Reference Variable to Memory Address
- Old JVM versions - in between table has the link to direct memory address. Every reference variable has an entry in the table.
- Compressed Ordinary Object Pointers (Compressed OOPS) - The references hold the actual address. But the address is an offset from the start of the heap address space. This avoids using 64 bit address pointers.
- Direct Pointer - References to the direct address in the heap.
Passing Reference in Methods
When object references are passed to methods, they're passed by value. This means that a copy of the reference is made, not the actual object. As a result, changes made to the object inside the method affect the original object, while changes to the reference itself such as assigning a different object to this reference don't affect the original reference.