Boolean Algebra
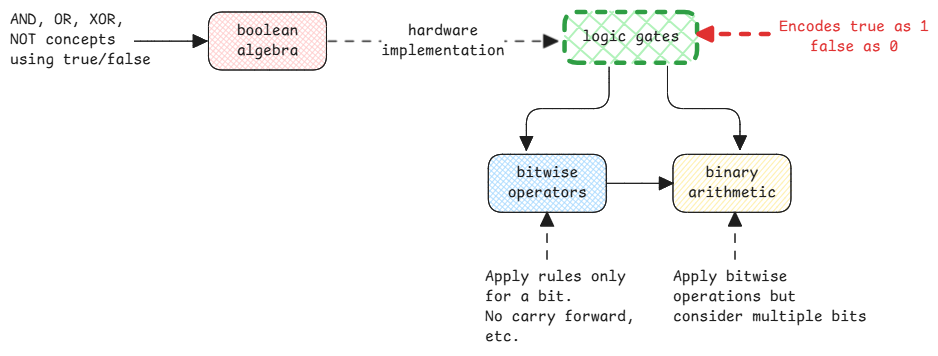
Boolean algebra is the original theoretical area dealing with only true and false. It's this area of mathematics that introduced AND, OR, XOR, NOT etc. concepts for boolean inputs.
This is the basis of bit-wise and binary-arithmetic fields. Computers at the end use different operators in boolean algebra to perform binary arithmetic.
This a very important mental model to have. Binary and boolean aren't same. It's just that the binary is used to represent boolean values.
Standard Boolean Operators
| Operator | Symbol | Description | Input causing output = True | Input causing output = False |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOT | ¬, ~ | Flips the value | Input = False | Input = True |
| AND | ∧, · | True only if both are true | Both True | Any False |
| OR | ∨, + | True if at least one is true | Any True | Both False |
| XOR | ⊕, ⊻ | True if inputs are different | Inputs differ | Inputs same |
| NAND | ↑, ⊼ | Opposite of AND | Any False | Both True |
| NOR | ↓, ⊽ | Opposite of OR | Both False | Any True |
| XNOR | ⊙, ≡ | True if inputs are the same | Inputs same | Inputs differ |
Bitwise operators aren't part of boolean algebra. Normally we refer everything as bitwise operations but they aren't actually.
Bit right/left shift, rotate right/left are bitwise operators.
Arithmetic Negation
Arithmetic negation is the negative number representation of a positive number. The most important mental model is to think in term of modular operation where used the circular based counter. For counting positive numbers, we move in clockwise direction starting form zero and for counting negative numbers, we move in the opposite direction starting from zero.
Since , negating will always generate the value that when added to the original value will bring the position of the pointer on the circular ring to zero. Hence the value of is always (. The is needed to ensure the counter comes to zero.
It's a very important mental model to remember that, numbers at CPU register level are placed in a circular ring. Meaning, it starts from 0 and goes up to depending on the size of the variable.
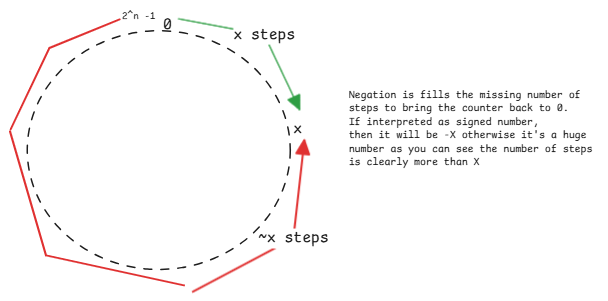
- Boolean NOT. Flips true to false and vice versa.
- Arithmetic negation - Subtracts a number from zero.
- Bitwise NOT - Flips every individual bit from 0 to 1 and 1 to 0.