Matrices
Matrix is an interesting topic since memory is just single dimensional. It's important to understand how multi dimensional matrices are represented in memory.
The core data structure used is the array. When we declare matrices, then nested arrays are used to represent the same.
It's important to keep in mind that matrices and arrays are used to represent the same concept. Both are same. Moreover the programming languages also use the arrays to implement matrices.
- A single dimensional matrix is just a normal array where values are just primitives.
- A two dimensional matrix is array of arrays where values are just pointers to underlying arrays.
- A three dimensional matrix is array of array of arrays.
This can be nested up to any levels required.
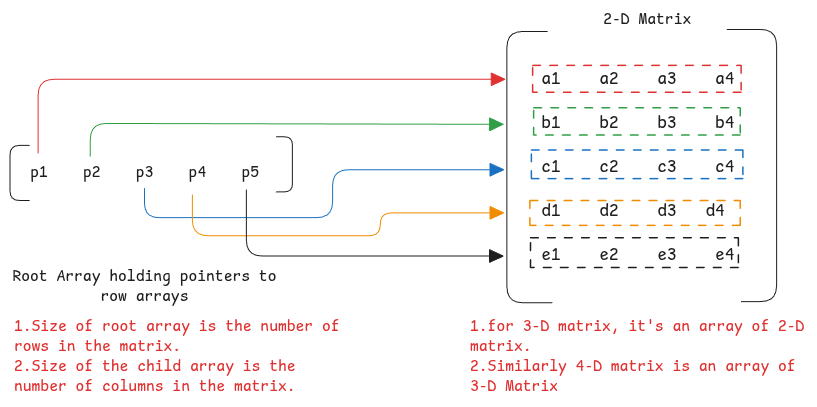
It's important to understand the structure of the matrices in terms of underlying arrays to calculate the size of the matrix in different dimensions.
Mental model for multi dimensional matrices
Its important to understand and remember how 1D and 2D matrices are represented in memory. The rest are just built on top of it by nesting multiple layers. Irrespective of the size of the matrix, at the end the actual matrix data is stored in 1-D matrix which is nothing but an array which is again just a continuous memory area holding primitive values.
N dimensional array is just an array where elements are just N-1 arrays. This goes until the elements becomes primitive types.
int[][][] A = {
{ // A[0] (first level)
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 }, // A[0][0] (second level)
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 }, // A[0][1]
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 } // A[0][2]
},
{ // A[1]
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 }, // A[1][0]
{ 17, 18, 19, 20 }, // A[1][1]
{ 21, 22, 23, 24 } // A[1][2]
}
};
int[][][][] A = {
{ // A[0] (first level)
{ // A[0][0] (second level)
{ 1, 2 }, // A[0][0][0] (third level)
{ 3, 4 }, // A[0][0][1]
{ 5, 6 } // A[0][0][2]
},
{ // A[0][1]
{ 7, 8 }, // A[0][1][0]
{ 9, 10 }, // A[0][1][1]
{ 11, 12 } // A[0][1][2]
}
},
{ // A[1]
{ // A[1][0]
{ 13, 14 },
{ 15, 16 },
{ 17, 18 }
},
{ // A[1][1]
{ 19, 20 },
{ 21, 22 },
{ 23, 24 }
}
}
};