Scopes
Scopes in Gradle are pretty much similar Maven except to one big difference between api and implementation. In Maven, we've just compile scope but in case of Gradle this is split into two.
- api - A dependency added with this scope will add even the transitive dependencies from the dependency to it's final jar.
- implementation - This means the dependency is an implementation detail of the module and won't be exported to consumers of the module. The producer of the module itself will compile since Gradle will ensure the classpath contains the dependencies.
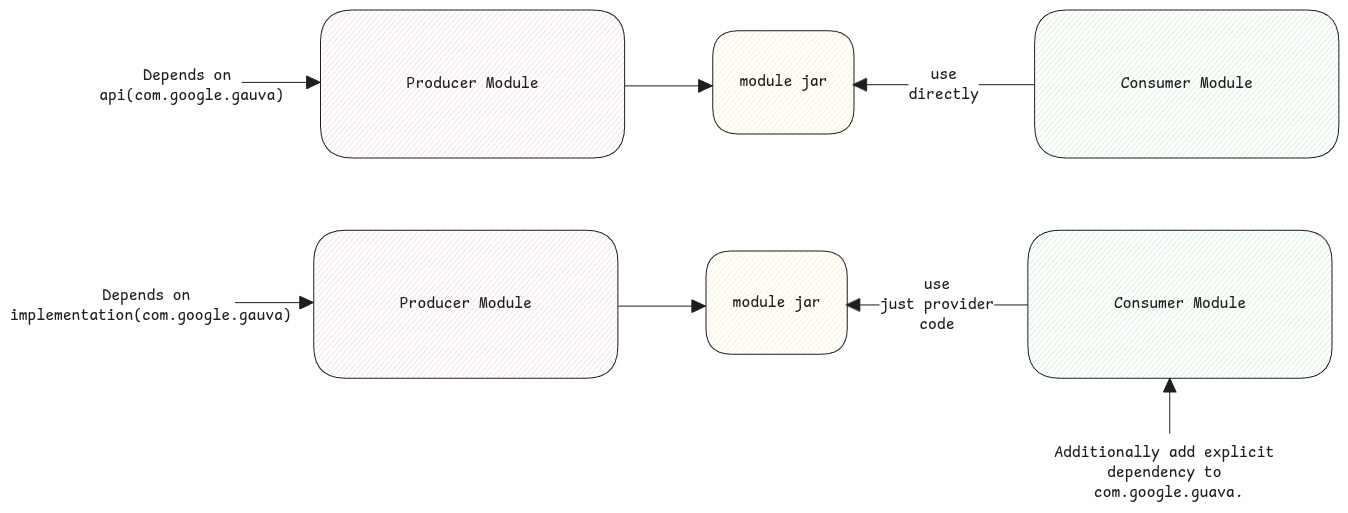
Initially when we hear the name api, it looks like it will only contain some APIs and no implementation.
But this is actually the opposite. Here when we say api, it means the producer decides to add the corresponding dependency to it's final jar.
This means, the api scoped dependencies are actually larger than the ones which have just implementation scope.
At runtime Gradle doesn't exist. Gradle will only ensure to build the jar accordingly and if there are any missing classes then the JVM will throw an error.
Test Fixtures
Gradle handles shared libraries related to tests differently. In Maven, we usually write all tests and shared code related to test under tests folder. Whereas in Gradle, we can use testFixtures folder for hosting all shared test code.
Test fixtures have their own scopes - testFixturesImplementation and testFixturesApi. These scopes works exactly like what api and implementation scopes does for productive code.
Gradle ensures such scoped dependencies are used only for the code in testFixtures folder. So on one side it brings in different classpath for test fixtures and at the same time, it will ensure what the consumers of the test fixtures module see.
- Productive code - sees only api and implementation dependencies.
- Test code - sees productive code plus testImplementation dependencies.
- Test fixtures code - sees only testFixturesImplementation and testFixturesApi dependencies.